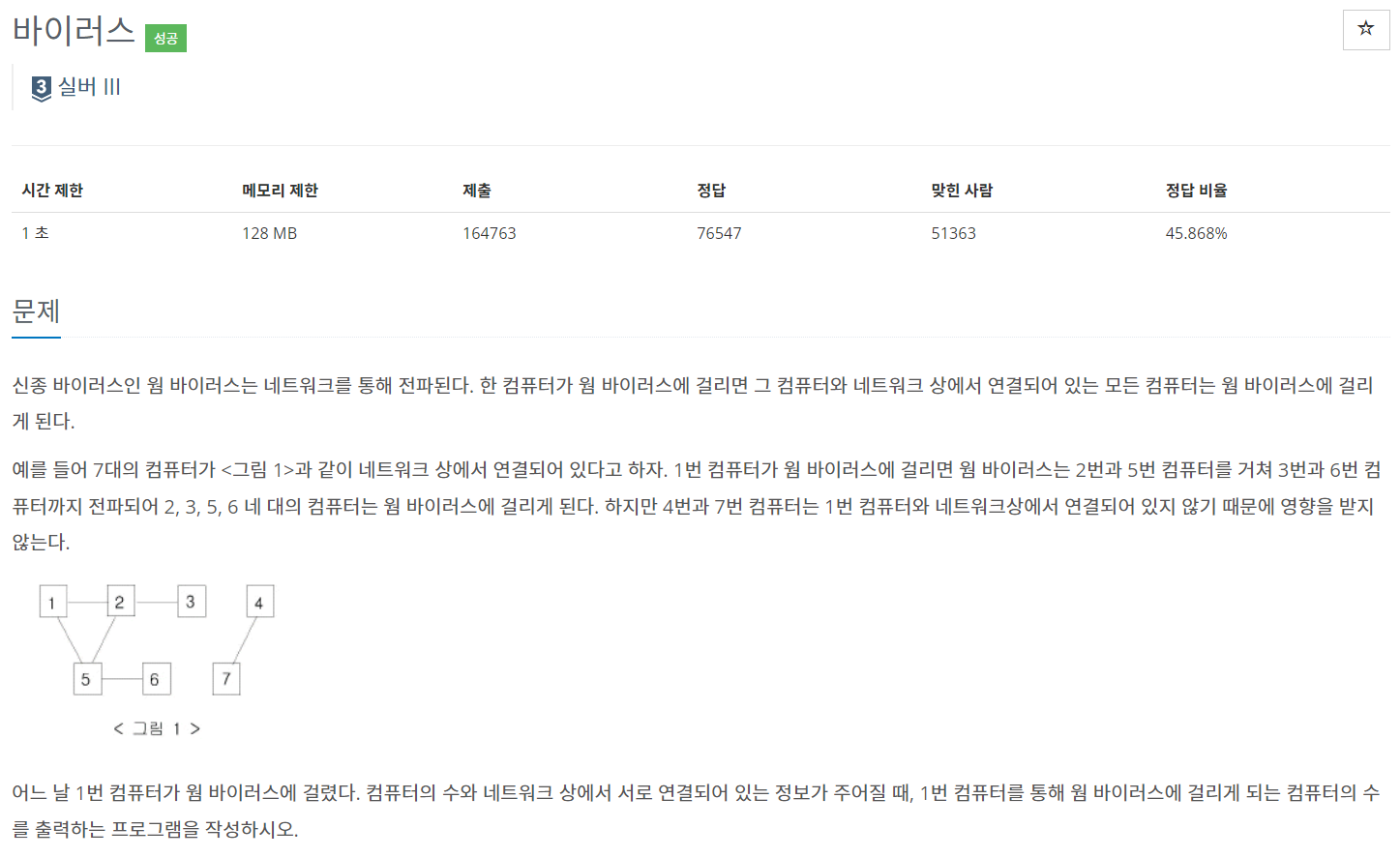
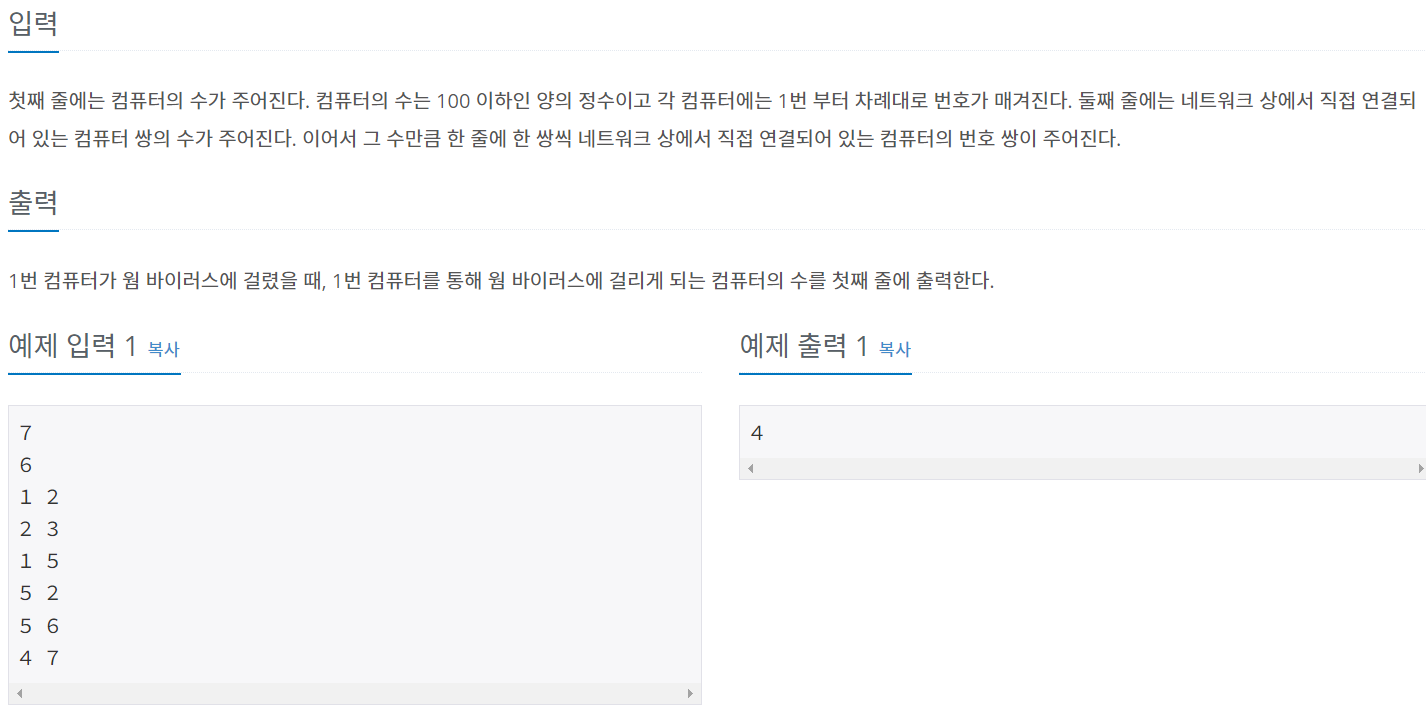
문제
문제 분석
- 1번 컴퓨터와 연결되어 있는 뭉텅이의 개수를 세는 문제이다.
- DFS/BFS을 통해 연결된 한 뭉텅이의 개수를 출력하면 된다.
정답 코드
// 1번과 연결된 뭉텅이의 크기를 찾는 문제 (BFS 풀이)
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
#define MAX_N 101 // N의 최댓값 : 100
int Board[MAX_N][MAX_N]; // 연결되었으면 1
int visited[MAX_N]; // 감염되었으면 1
int node;
void bfs(int start_node) {
int ans = 0; // 바이러스에 감염된 컴퓨터 수
queue<int> q;
// 초기 감염 컴퓨터 처리
q.push(start_node);
visited[start_node] = 1;
while (!q.empty()) {
int cur_node = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int next_node = 1; next_node <= node; next_node++) {
if (Board[next_node][cur_node] != 1) continue; // 연결되지 않은 경우 다음 노드가 될 수 없음
if (visited[next_node] != 0) continue; // 이미 감염된 컴퓨터는 방문할 필요가 없음
// 다음 감염될 컴퓨터 조건에 해당하는 경우 처리
q.push(next_node);
visited[next_node] = 1;
ans++;
}
}
cout << ans; // 최종적으로 바이러스에 감염된 컴퓨터 수 출력
}
int main(void) {
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(nullptr);
int edge;
cin >> node;
cin >> edge;
for (int i = 0; i < edge; i++) {
int start, end;
cin >> start >> end;
Board[start][end] = Board[end][start] = 1; // 서로 연결되었다는 것을 의미
}
bfs(1);
return 0;
}교훈점
- 간선의 가중치가 동일하고 서로 연결되어 있는 것을 찾는 문제는 DFS/BFS 문제이다.



